You’re in the right place to learn about music note values (duration), which are determined by the type (shape) of musical notes (whole notes, half notes, etc.).
The combination of music notes values creates rhythm.
SHOW/HIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS
7 Note Values
Learn How to Read Your First Music Note in 1 Minute!
Choose your 4K Video: A B C D E F G or Do Re Mi Fa Sol La Ti
There are 7 note values (and 7 musical rests of the same duration): the Whole Note, the Half Note, the Quarter Note, the Eight Note, the Sixteenth Note, the Thirty-Second Note, the Sixty-Fourth Note.

The beginning of Beethoven’s Piano Sonata No. 3 uses the Whole Note, the Half Note, the Quarter Note, the Eight Note, the Sixteenth Note, the Eight Note triplet:
Rhythmic Equivalences Between the Different Note Values
The value of each note duration is always double the value that follows it:
- 1 Whole Note = 2 Half Notes
- 1 Half Note = 2 Quarter Notes
- 1 Quarter Note = 2 Eight Notes
- 1 Eight Note = 2 Sixteenth Notes
- 1 Sixteenth Note = 2 Thirty-Second Notes
- 1 Thirty-Second Note = 2 Sixty-Fourth Notes
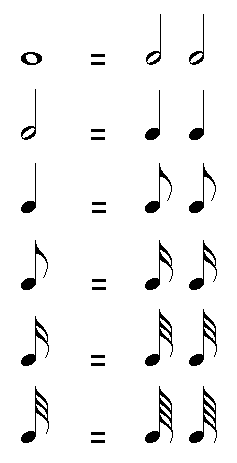
And so:
A Whole Note = 4 Quarter Notes, 8 Eight Notes, 16 Sixteenth Notes, 32 Thirty-Second Notes, 64 Sixty-Fourth Notes
A Half Note = 4 Height Notes, 8 Sixteenth Notes, 16 Thirty-Second Notes, 32 Sixty-Fourth Notes
A Quarter Note = 4 Sixteenth Notes, 8 Thirty-Second Notes, 16 Sixty-Fourth Notes
A Eight Note = 4 Thirty-Second Notes, 8 Sixty-Fourth Notes
A Sixteenth Note = 4 Sixty-Fourth Notes
This Video Is a Game! Play With It to Learn How to Read the Notes!
Syllabic version: Do Re Mi Fa Sol La (Ti)British Names
- Whole Note = Semibreve
- Half Note = Minim
- Quarter Note = Crotchet
- Eight Note = Quaver
- Sixteenth Note = Semiquaver
- Thirty-Second Note = Demisemiquaver
- Sixty-Fourth Note = Hemidemisemiquaver
Dotted Notes
A dot behind a music note increases the duration of this note by half of its original value.
For example, as 1 Half Note = 2 Quarter Notes, half of a Half Note = 1 quarter note. So, the duration for 1 dotted Half Note will be 2 Quarter Notes + 1 Quarter Note = 3 Quarter Notes.
The value of the dotted notes for each type of music note is as follow:
- 1 dotted Whole Note = 3 Half Notes
- 1 dotted Half Note = 3 Quarter Notes
- 1 dotted Quarter Note = 3 Eight Notes
- 1 dotted Eight Note = 3 Sixteenth Notes
- 1 dotted Sixteenth Note = 3 Thirty-Second Notes
- 1 dotted Thirty-Second Notes = 3 Sixty-Fourth Notes
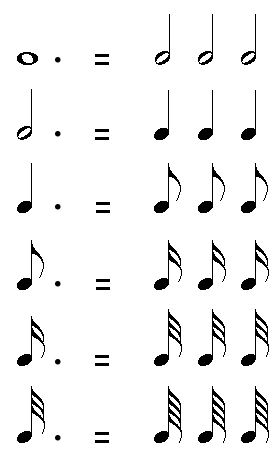
Triplet
A triplet is the ternary division of a note value. It is a rhythm playing three notes in the space of two.
For example, a quarter note triplet consists of three-quarter notes over the same amount of time as two-quarter notes or a single half note
The famous Adagio from Beethoven’s sonata no. 14, called “Moonlight”, uses eighth-note triplets on each beat, from the first to the last measure. This is the reason why the number 3 which indicates a triplet is only present here in the first measure of the Adagio (play the video to display the first measure, the number 3 indicating a triplet is placed under the group of three eighth notes ):
Music Notes in Space HN
A FREE Video Game to learn note values the fun way. Music Notes In Space HN makes it easy to learn and remember what shape of music note corresponds to what relative value as well as the ratio of any note value to any other.
Happy Note!’s Links about Music Duration and Music Theory
Learn more about music duration and music theory by following the links below:
Music Staff (or Stave)
The music staff (or stave) is made by five parallel horizontal lines.
Clefs – Treble, Bass, Alto, Tenor
Learn about the different musical clefs and which one is used for each musical instrument.
Music Notes – Name of Notes (A B C or Do Re Mi)
7 notes of music and two systems to name them.
Music Rests (Whole Rest, Half Rest…)
For each music note value, there is a music rest of equivalent duration.