Whole rest, half rest… Learn to recognize the 7 musical rests and the corresponding durations of the 7 notes values (whole note, half note…) they represent.
In music, musical rests denote brief silences, serving as short breaks in the flow of sound. In musical notation, a rest is the symbol that signifies such a pause.
This Video Is a Game! Play With It to Learn How to Read the Notes!
More videos: Do Re Mi Fa Sol La Ti (instead of Si) and A B C D E F GJust as there are music notes of different values (whole note, half note, etc.), there are rests of different values (whole rest, half rest…).
For each note value, there is a rest of equivalent value; and for each rest value, there is a note of equivalent value.
SHOW/HIDE TABLE OF CONTENTS
Music Rests of Different Values
The example below shows how some of the music notes making up a musical phrase can be replaced with music rests of equivalent lengths.
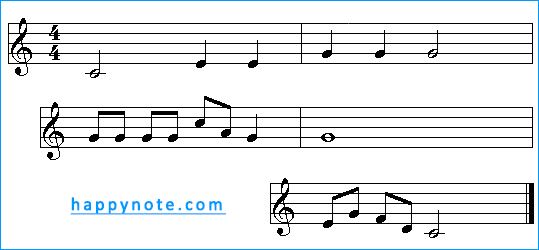
Now, the same musical phrase, but some music notes have been changed in rests:
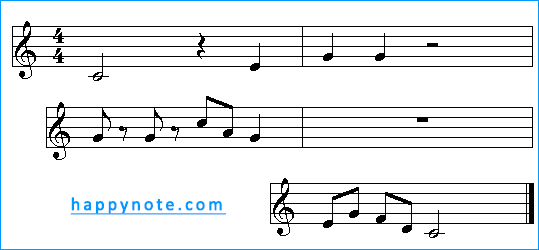
Note Value and Silence of an Equivalent Duration
There is a musical silence for each value of note
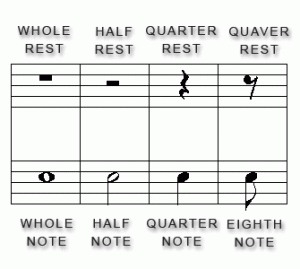
The whole rest, which is positioned below the fourth line of the staff – remember, lines on the musical staff are always counted from the bottom up – represents a musical rest lasting the same duration as a whole note.
IMPORTANT: When indicating silence for an entire measure, always use a whole rest symbol, regardless of the measure’s duration. For instance, if the piece is written in 3/4 time (meaning it consists of three beats per measure, each worth a quarter note), even though three quarter notes equal a dotted half note rather than a whole note, you should still use a whole rest symbol to indicate the silence.
The half rest, positioned on the third line of the staff, equals the duration of a half note.
The quarter rest equals the duration of a quarter note.
The eighth rest equals the duration of the eight note, the sixteenth rest equals the duration of the sixteenth note, the thirty-second rest equals the duration of the thirty-second note, and the sixty-fourth rest equals the duration of the sixty-four note.
Difference Between American English and British English
AMERICAN ENGLISH – BRITISH ENGLISH
- Whole Rest – Semibreve Rest
- Half Rest – Minim Rest
- Quarter Rest – Crotchet Rest
- Eight Rest – Quaver Rest
Dotted Rest
The duration of a rest may be increased by half but it’s reserved to modern music.
Learn Music Rests the Fun Way with the Free Game Music Note Cracker HN
Music Rests and Music Theory
Music Staff (or Stave)
The music staff (or stave) is made by five parallel horizontal lines.
Clefs – Treble, Bass, Alto, Tenor
Learn about the different musical clefs and which one is used for each musical instrument.
Music Notes – Name of Notes (A B C or Do Re Mi)
Seven notes of music and two systems to name them.