The note value (duration) of a note is determined by its shape — or figure.
The combination of different note values creates the musical rhythm (not to be confused with tempo, which refers to the overall speed of the music).
The 7 Common Note Values
There are 7 main note values (and 7 musical rests of the same duration): the Whole Note, the Half Note, the Quarter Note, the Eighth Note, the Sixteenth Note, the Thirty-Second Note, the Sixty-Fourth Note.

The beginning of Beethoven’s Piano Sonata No. 3 uses the whole note, the half note, the quarter note, the eighth note, the sixteenth note, and the eighth note triplet (see below). Note that consecutive sixteenth notes are shown by connecting them with two horizontal beams, eighth notes with one beam (thirty-second notes would use three beams, sixty-fourth notes four).
Le texte italien Allegro con brio juste au-dessus de la portée en haut à gauche est une indication de tempo et de caractère précisant que la musique de Beethoven doit être jouée rapidement avec brio.
Notes Value and Rests
Just as there are music notes of different values (whole note, half note, etc.), there are rests of different values (whole rest, half rest…).
To learn about musical rests and their equivalence with note values, visit the page 7 Music Rests: Whole Rest, Half Rest, Quarter Rest…
Rhythmic Equivalences Between the Different Note Values
The value of each note duration is always double the value that follows it:
- 1 Whole Note = 2 Half Notes
- 1 Half Note = 2 Quarter Notes
- 1 Quarter Note = 2 Eighth Notes
- 1 Eighth Note = 2 Sixteenth Notes
- 1 Sixteenth Note = 2 Thirty-Second Notes
- 1 Thirty-Second Note = 2 Sixty-Fourth Notes
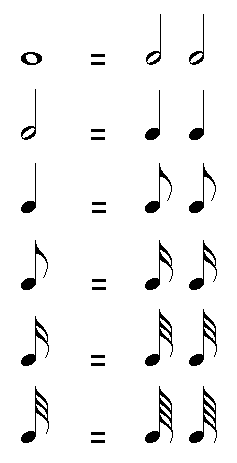
And so:
- A Whole Note = 4 Quarter Notes, 8 Eighth Notes, 16 Sixteenth Notes, 32 Thirty-Second Notes, 64 Sixty-Fourth Notes
- A Half Note = 4 Eighth Notes, 8 Sixteenth Notes, 16 Thirty-Second Notes, 32 Sixty-Fourth Notes
- A Quarter Note = 4 Sixteenth Notes, 8 Thirty-Second Notes, 16 Sixty-Fourth Notes
- An Eighth Note = 4 Thirty-Second Notes, 8 Sixty-Fourth Notes
- A Sixteenth Note = 4 Sixty-Fourth Notes
British Names
In British English and in countries like Australia and New Zealand, note values have distinct names that differ from American terminology:
- Whole Note = Semibreve
- Half Note = Minim
- Quarter Note = Crotchet
- Eighth Note = Quaver
- Sixteenth Note = Semiquaver
- Thirty-Second Note = Demisemiquaver
- Sixty-Fourth Note = Hemidemisemiquaver
Dotted Notes
A dot behind a music note increases the duration of this note by half of its original value.
For example, as 1 Half Note = 2 Quarter Notes, half of a Half Note = 1 quarter note. So, the duration for 1 dotted Half Note will be 2 Quarter Notes + 1 Quarter Note = 3 Quarter Notes.
The value of the dotted notes for each type of music note is as follow:
- 1 dotted Whole Note = 3 Half Notes
- 1 dotted Half Note = 3 Quarter Notes
- 1 dotted Quarter Note = 3 Eighth Notes
- 1 dotted Eighth Note = 3 Sixteenth Notes
- 1 dotted Sixteenth Note = 3 Thirty-Second Notes
- 1 dotted Thirty-Second Notes = 3 Sixty-Fourth Notes
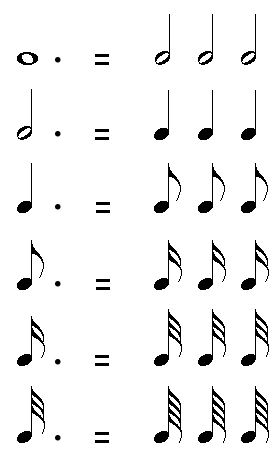
The pair “dotted eighth note–sixteenth note” is used extremely frequently in music. The eleventh piece of Carnaval by Schumann, Chiarina, is a perfect example:
The score of Chiarina uses the quarter note, the half note, the dotted eighth note, and the sixteenth note. In addition, the quarter notes are tied to the dotted eighth notes, so they are held but not played again (tie).
The tie of two identical notes
When two notes of the same pitch and name are tied, the second note is held but not played again, which allows the composer to create as many rhythms and note durations as desired.
Thus, in Chiarina above, the quarter notes of the melody in the right hand are tied to the following dotted eighth notes and are therefore held but not played again.
Triplet
A triplet is the ternary division of a note value. It is a rhythm playing three notes in the space of two.
For example, a quarter note triplet consists of three-quarter notes over the same amount of time as two-quarter notes or a single half note
The famous Adagio from Beethoven’s sonata no. 14, called “Moonlight”, uses eighth-note triplets on each beat, from the first to the last measure. This is the reason why the number 3 which indicates a triplet is only present here in the first measure of the Adagio (play the video to display the first measure, the number 3 indicating a triplet is placed under the group of three eighth notes ):
The number 3 above groups of three eighth notes indicates a triplet.
Duplet and Tuplets
Like the triplet, the duplet is part of the broader family of tuplets, which are irregular groupings of notes played in the time normally allotted to a different number.
A duplet is essentially the reverse of a triplet — a binary division within a ternary context.
Music theory concepts related to note duration
Note Value and Time Signature
While the organization of different note values forms the foundation of rhythm, the time signature (or measure signature) specifies how many beats each measure contains and which note value represents a single beat. Understanding the relationship between note values and the time signature allows musicians to read and perform music with accurate timing.
Rhythm, tempo, and metronome
If rhythm is created by the succession of note values (whole note, half note, quarter note, eighth note…), it is the tempo that determines the speed. Although these two concepts are distinct, rhythm and tempo (set by the metronome) are inseparable for performing a score, as one can only be expressed in relation to the other to give the music its flow and character.
Music Notes in Space HN: Learn Note Value the Fun Way
A free video game to learn note values the fun way. Music Notes In Space HN makes it easy to learn and remember what shape of music note corresponds to what relative value as well as the ratio of any note value to any other.